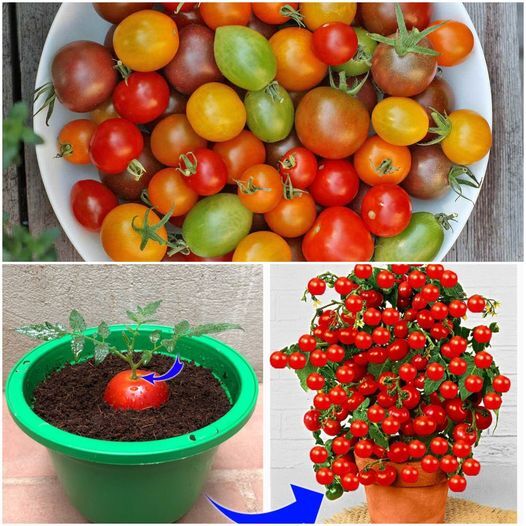
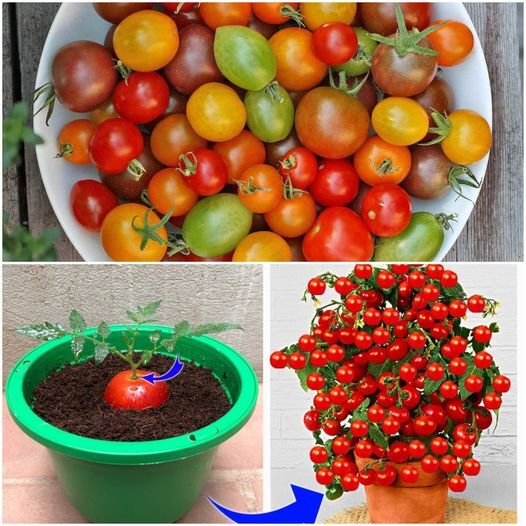
Tomatoes are a beloved addition to many gardens, offering juicy, flavorful fruits that enhance any meal. While most people are familiar with growing tomatoes from seeds or buying young plants, few know about an incredibly simple and effective method: propagating tomatoes from cuttings. This technique is not only easy but also a fantastic way to ensure you have a continuous supply of tomato plants. Here’s how you can do it and why it’s worth trying.
Why Propagate from Cuttings?
Propagating tomatoes from cuttings has several advantages:
-
Faster Growth: Cuttings grow faster than seeds because they are already a part of a mature plant.
-
Genetic Consistency: You get an exact clone of the parent plant, ensuring the same quality and taste.
-
Cost-Effective: It’s a free way to multiply your plants if you already have a healthy tomato plant.
What You Need
-
A healthy tomato plant
-
Sharp scissors or pruning shears
-
A glass of water
-
Small pots with potting soil
-
Optional: rooting hormone
How to Propagate Tomatoes from Cuttings
1. Select a Healthy Plant:
-
Choose a strong, healthy tomato plant with no signs of disease or pest damage. Look for sturdy, non-flowering stems.
2. Take the Cutting:
-
Using sharp scissors or pruning shears, cut a 6-8 inch section of a non-flowering stem. Make sure to cut just below a leaf node, as this is where new roots will form.
3. Prepare the Cutting:
-
Remove the lower leaves from the cutting, leaving a few leaves at the top. If you have rooting hormone, dip the cut end into it to encourage faster root growth.
4. Root the Cutting in Water:
-
Place the cutting in a glass of water, ensuring that the bottom half is submerged. Change the water every few days to keep it fresh and prevent rot. In about one to two weeks, you should see roots starting to develop.
5. Transplant to Soil:
-
Once the roots are about an inch long, transplant the cutting into a small pot filled with potting soil. Water it well and place it in a sunny spot. Keep the soil moist but not waterlogged.
6. Care for the New Plant:
-
After a few weeks, when the plant has established strong roots and new growth, it can be transplanted into your garden or a larger pot.
Benefits of Propagating Tomatoes from Cuttings
-
Quick Turnaround: You’ll have new tomato plants ready to produce fruit faster than starting from seeds.
-
Disease Management: This method allows you to perpetuate plants that are resistant to diseases prevalent in your area.
-
Space Efficiency: If you have limited space, this is a great way to start multiple plants without using up garden space for seed starting.
Conclusion
Propagating tomatoes from cuttings is a lesser-known but highly effective method to expand your tomato garden. It’s easy, cost-effective, and ensures you have robust, productive plants. Give this technique a try, and you’ll be enjoying a bountiful harvest of delicious tomatoes in no time!