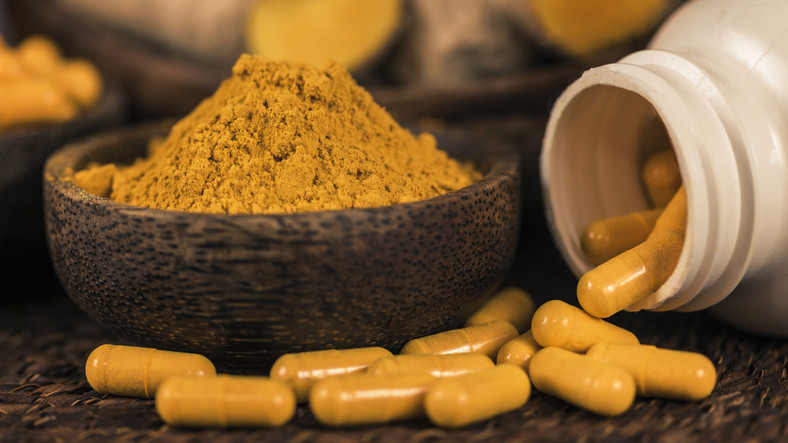
In the vibrant world of spices, turmeric shines as a golden beacon of health and wellness. Often hailed for its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, this bright yellow spice has been a staple in culinary and medicinal traditions around the globe. But when we delve deeper into the magic of turmeric, we encounter a star component: curcumin. Let’s explore the relationship between turmeric and curcumin, shedding light on how they differ and the unique benefits each offers.
Turmeric: The Golden Spice
Turmeric is a root, or rhizome, of the Curcuma longa plant, belonging to the ginger family. Its ground form is a key ingredient in many dishes, imparting a warm, bitter taste and a distinctive yellow color. Beyond its culinary uses, turmeric has been revered in traditional medicine for thousands of years, particularly in Ayurveda and Chinese medicine, for its healing properties.
Curcumin: The Active Compound
Curcumin is the principal curcuminoid found in turmeric, responsible for the spice’s vibrant color and many of its health benefits. It’s a bioactive compound that has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and therapeutic properties. However, curcumin makes up only a small percentage of turmeric, approximately 2-6%, which brings us to the heart of their differences.
Comparing Benefits and Uses
While turmeric and curcumin share many health benefits due to curcumin’s presence in turmeric, their potency and applications can differ significantly:
-
Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties: Curcumin is highly potent in its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant actions, more so than turmeric. It’s often extracted and used in supplements for concentrated health benefits, particularly for joint health and reducing inflammation-related discomfort.
-
Culinary Uses: Turmeric, with its mild flavor and coloring properties, is widely used in cooking and as a natural food dye. Its health benefits, though less concentrated than curcumin supplements, are still significant, especially when consumed regularly as part of a healthy diet.
-
Absorption and Bioavailability: One challenge with curcumin is its low bioavailability; it’s not easily absorbed by the body when taken alone. Turmeric, on the other hand, contains natural oils that can enhance curcumin’s absorption. Furthermore, combining turmeric or curcumin with black pepper, which contains piperine, can significantly increase absorption, making the beneficial compounds more readily available to the body.
Incorporating into Your Lifestyle
For those looking to harness the health benefits of turmeric and curcumin, incorporating turmeric into your daily diet can be a delightful and healthful practice. Adding turmeric to soups, stews, smoothies, and teas not only enhances flavor and color but also contributes to your overall well-being. For more concentrated benefits, particularly for addressing specific health concerns, curcumin supplements may be an effective option, ideally taken with black pepper for enhanced absorption.
Turmeric and curcumin together offer a powerful duo of health benefits. Whether you’re sprinkling turmeric on your meals or taking a curcumin supplement, you’re embracing a time-honored tradition of natural healing and wellness.