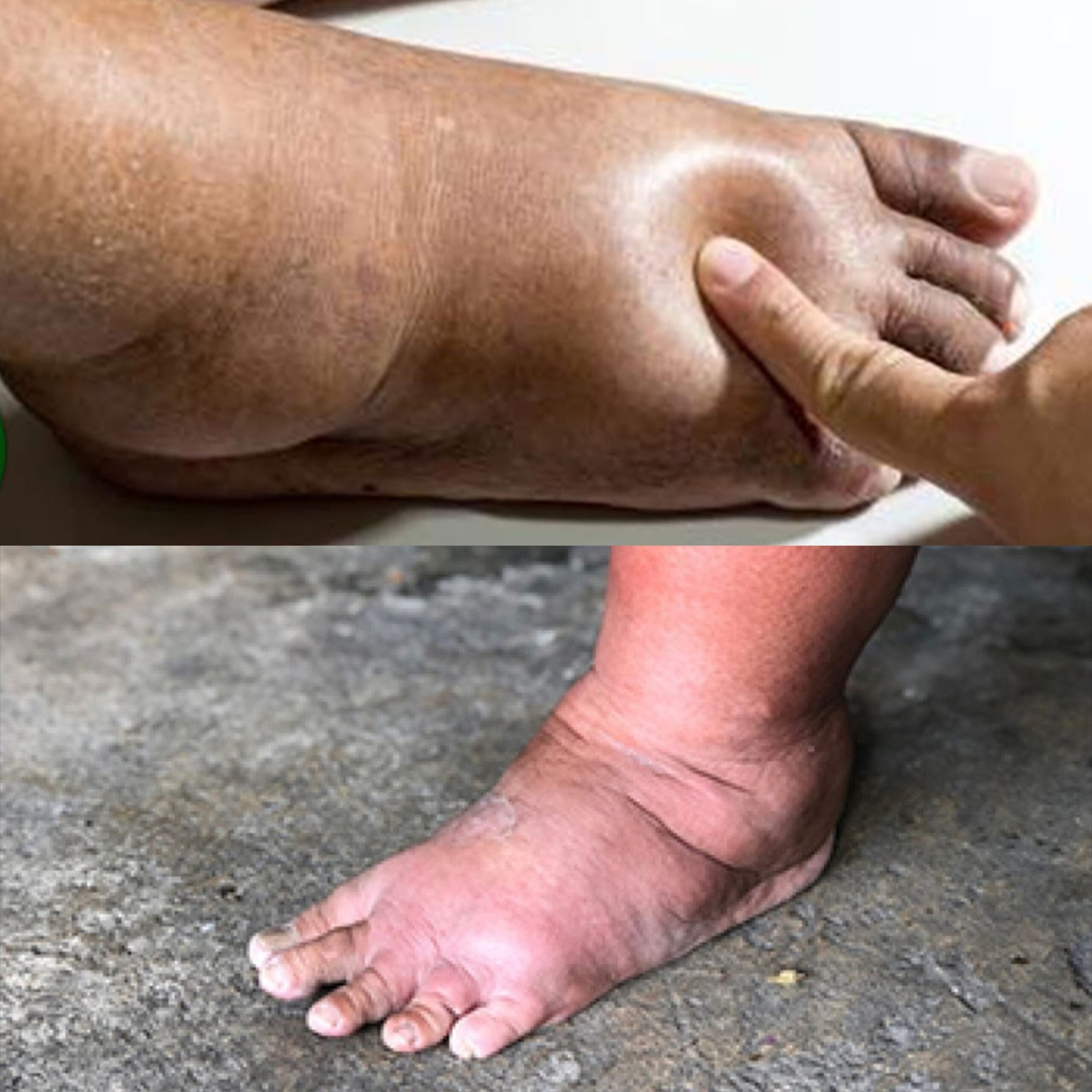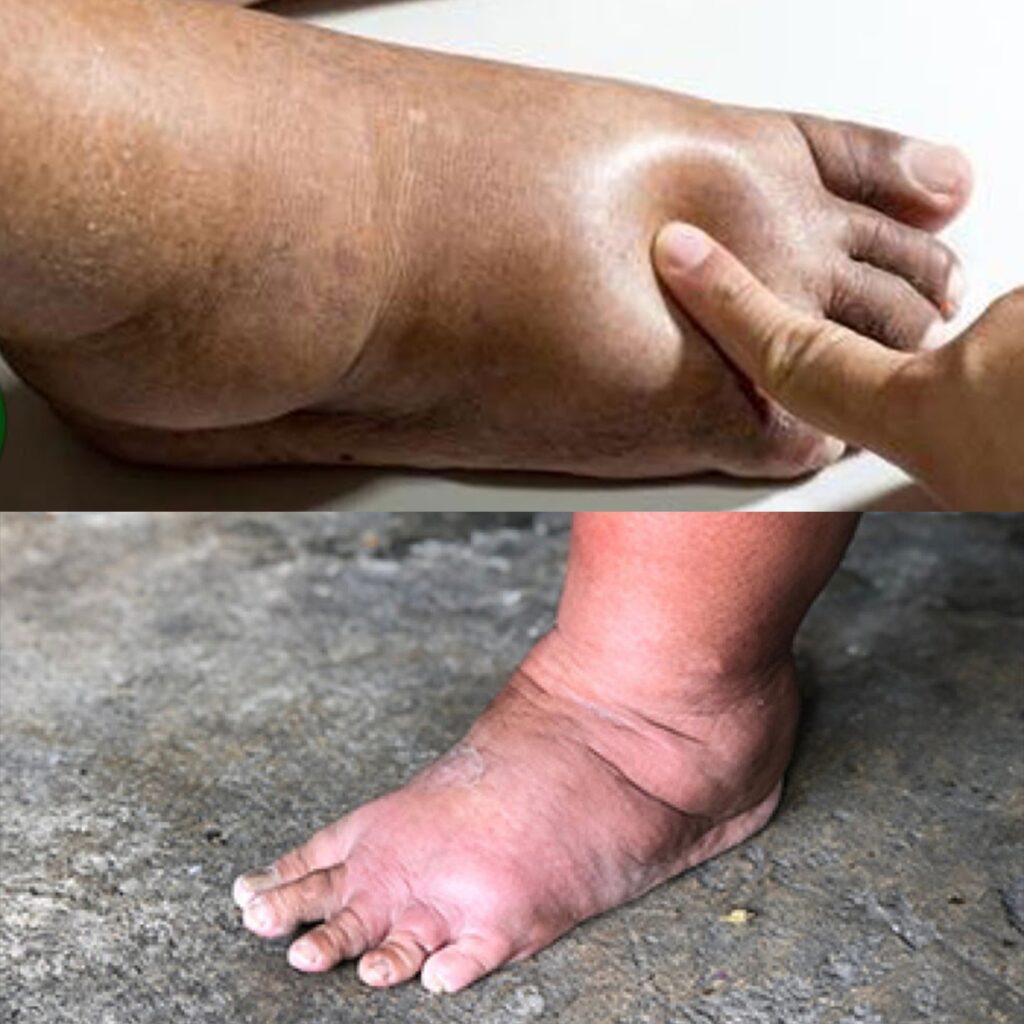
Swelling in the legs can be a common and sometimes distressing issue. It often leads to discomfort and concern about underlying health conditions. Generally, leg swelling can be attributed to two main factors: water retention and inflammation. Let’s explore these causes and understand how they might be affecting you.
Water Retention: A Common Culprit
Water retention, also known medically as edema, is often a primary reason for swelling in the legs. This condition occurs when excess fluid builds up in your body tissues. Several factors can lead to water retention, including:
-
Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Staying in one position for too long can hinder the normal circulation of blood and bodily fluids.
-
Salt Intake: Consuming too much salt can cause the body to retain water.
-
Certain Medications: Some drugs, like blood pressure medications and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can increase the likelihood of retaining water.
-
Medical Conditions: Heart conditions, kidney problems, and chronic venous insufficiency are health issues that can lead to increased water retention.
Inflammation: The Body’s Response to Injury
Inflammation is another key factor that can cause leg swelling. This natural response by your immune system can occur due to various triggers:
-
Injury: Sprains or fractures can lead to localized swelling as the body attempts to heal.
-
Infection: An infection in the leg can result in swelling and redness.
-
Chronic Diseases: Conditions like arthritis and gout involve inflammation, which can cause significant swelling in the affected areas.
Managing Swelling in Your Legs
Managing leg swelling effectively often depends on identifying the cause. Here are some general tips that can help manage both water retention and inflammation:
-
Elevate Your Legs: Lifting your legs above heart level several times a day can help improve circulation and reduce swelling.
-
Exercise Regularly: Gentle activities like walking or swimming can improve blood flow and help reduce fluid buildup.
-
Monitor Your Diet: Reducing salt intake and eating anti-inflammatory foods like berries, nuts, and leafy green vegetables can help manage edema and inflammation.
-
Stay Hydrated: Oddly enough, drinking plenty of water helps reduce water retention and flush out excess sodium.
-
Consult a Doctor: If swelling persists, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider to rule out or treat any underlying conditions.
Conclusion
If you’re experiencing swelling in your legs, understanding whether it’s due to water retention or inflammation is key to addressing the problem effectively. With proper lifestyle adjustments and medical advice, you can manage swelling and improve your comfort and health.