Magnesium is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the human body, including those involved in the synthesis of fat, protein, nucleic acids, and neurotransmitters, regulation of blood sugar and blood pressure, muscle and nerve functions, and calcium balance. Despite its importance, magnesium deficiency is relatively common. Here are 10 warning signs that may indicate your body needs more magnesium.
1. Muscle Cramps and Spasms
-
One of the most common signs of magnesium deficiency is frequent muscle cramps and spasms. Magnesium helps regulate neuromuscular signals and muscle contractions.
2. Persistent Fatigue
-
Low magnesium levels can lead to decreased energy production in the body, resulting in feelings of fatigue and weakness.
3. Mental Disorders
-
Deficiency in magnesium can manifest as anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders. Magnesium is crucial for maintaining brain function and stabilizing mood.
4. High Blood Pressure
-
Studies have shown that magnesium helps regulate blood pressure. A consistent lack of magnesium in your diet can contribute to high blood pressure.
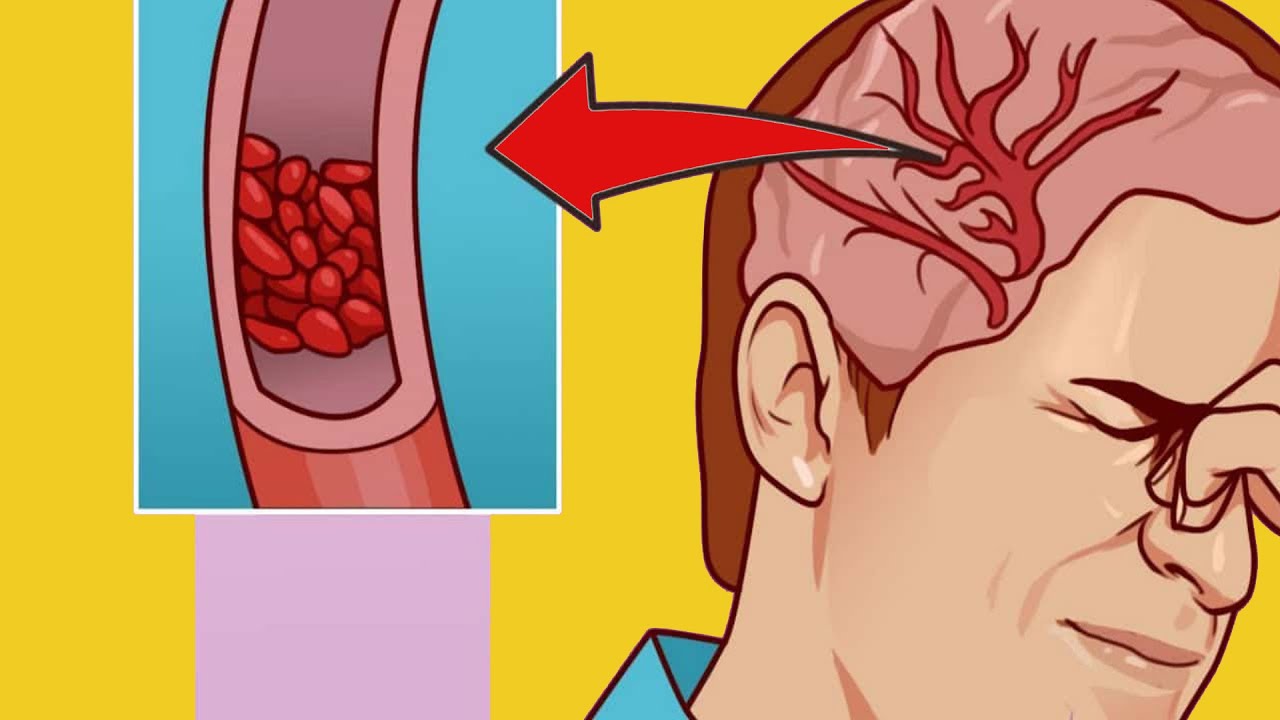
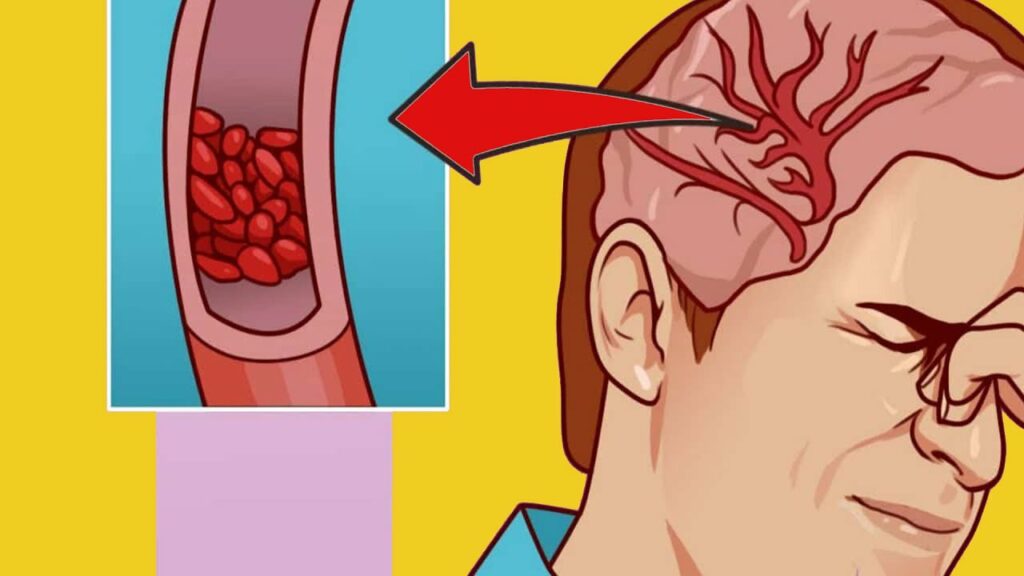
5. Irregular Heartbeat
-
Magnesium plays a key role in heart health. Low levels can cause irregular heartbeats or arrhythmias, which can be serious if not addressed.
6. Bone Health Issues
-
While calcium is crucial for bone health, magnesium is also essential. It activates vitamin D in the kidneys, which helps your body absorb calcium. A deficiency can lead to weaker bones and conditions like osteoporosis.
7. Constipation
-
Magnesium helps relax the muscles in the intestines, promoting bowel movements. Insufficient magnesium can result in constipation.
8. Numbness and Tingling
-
Insufficient magnesium can cause nerve dysfunction, leading to uncomfortable sensations like numbness and tingling in different parts of the body.
9. Headaches and Migraines
-
Magnesium deficiency is often linked to headaches and migraines. Increasing magnesium intake can help reduce these occurrences.
10. Insomnia or Poor Sleep
-
Magnesium plays a role in supporting deep, restorative sleep by maintaining healthy levels of GABA, a neurotransmitter that promotes sleep. Low magnesium levels can interfere with sleep.
How to Increase Magnesium Intake
To boost your magnesium levels, focus on incorporating more magnesium-rich foods into your diet:
-
Green leafy vegetables (e.g., spinach, kale)
-
Nuts and seeds (e.g., almonds, pumpkin seeds)
-
Whole grains (e.g., brown rice, whole wheat)
-
Legumes (e.g., black beans, chickpeas)
-
Dark chocolate (at least 70% cocoa)
If dietary changes are not sufficient, consider discussing magnesium supplements with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and type that could benefit you.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of magnesium deficiency is crucial for maintaining optimal health. By addressing a lack of magnesium early, you can prevent more serious health issues and improve your overall wellbeing. If you suspect you are deficient, consult with a healthcare professional who can recommend the best course of action based on your specific needs.