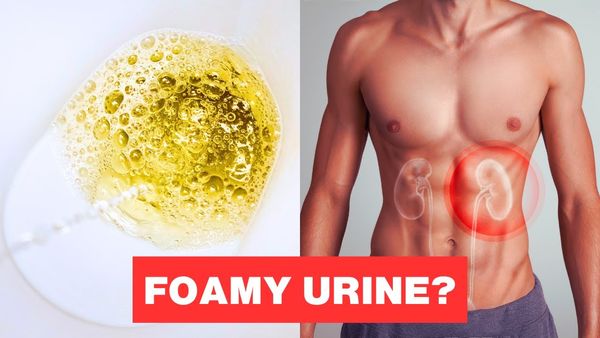
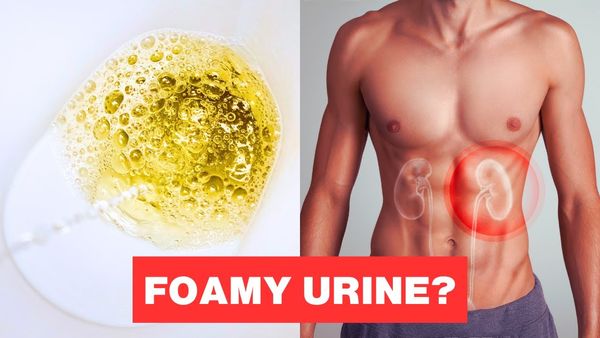
Don’t be alarmed if you notice foamy urine. In some cases, it could be a sign of a serious health issue called proteinuria, which involves high levels of protein in the urine. This condition can be an early indication of kidney disease. It’s essential to understand what foamy urine means and when it’s necessary to consult a healthcare professional.
What Causes Foamy Urine?
There are several reasons why your urine may appear foamy:
Excess Protein (Proteinuria):
- Proteinuria is the most common cause of persistent foamy urine. Normally, healthy kidneys do not allow a significant amount of protein to pass into the urine. If protein is present in your urine, it could indicate kidney damage or disease.
Speed and Force of Urination:
- Sometimes, urine may appear foamy if it hits the toilet at a high speed. Although this can be startling, it is generally harmless and temporary.
Dehydration:
- When you are dehydrated, your urine can become concentrated, causing it to appear more foamy than usual. Increasing your fluid intake can help alleviate this issue.
Chemical Contaminants:
- Substances found in toilet cleaners or other chemicals used in the bathroom can sometimes make urine foamy. Flushing the toilet before urination may eliminate the problem if this is suspected.
When to See a Doctor
It is crucial to monitor any changes in the characteristics of your urine. You should consult a healthcare provider if:
- The foamy urine persists over several days without an obvious cause, such as dehydration.
- You observe additional symptoms, such as swelling around your legs and eyes, which could indicate kidney damage.
- You have existing health conditions that might contribute to kidney issues, such as diabetes, hypertension, or previous kidney problems.
Tests and Diagnosis
If you experience foamy urine and seek medical attention, your doctor may recommend the following tests:
- Urine Tests: A simple urine analysis can detect excess protein in your urine.
- Blood Tests: These tests can assess how well your kidneys are functioning and check for signs of diabetes and other related health issues.
- Kidney Ultrasound: An imaging test to evaluate the size, shape, and position of your kidneys.
Prevention and Management
If you are diagnosed with proteinuria or any kidney issue, the management plan may involve:
- Dietary Changes: Your healthcare provider might recommend reducing protein intake, along with maintaining a balanced fluid intake.
- Medication: Medications to manage high blood pressure and diabetes can help address the underlying causes of kidney stress.
- Regular Monitoring: It is important to keep track of kidney function with regular visits to your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Don’t ignore foamy urine, especially if it occurs frequently or is accompanied by other symptoms. Although it can be benign, caused by minor factors like dehydration or forceful urination, it often warrants a check-up to rule out proteinuria or kidney damage. Timely treatment and management are crucial for maintaining your health and preventing complications. Remember, it’s always better to be safe than sorry.