Leg swelling can be uncomfortable and concerning, and it’s important to understand the potential causes behind it. Swelling in the legs can result from water retention (also known as edema) or inflammation, and sometimes both. Identifying the cause is crucial for proper treatment and management. Here are some common reasons why your legs might swell and how to differentiate between water retention and inflammation:
Water Retention (Edema)
Causes:
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Being in one position for too long can cause fluids to pool in the leg veins, not allowing them to return to the heart efficiently.
- Salt Intake: Consuming high amounts of salt can cause the body to retain more fluid.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as those for high blood pressure or steroids, can cause increased fluid retention.
- Heart Conditions: If the heart does not pump blood effectively (as in the case of heart failure), it can cause fluid to build up in the legs and other parts of the body.
- Kidney or Liver Disease: Problems with kidney or liver function can lead to fluid imbalance and swelling in various parts of the body, including the legs.
Symptoms:
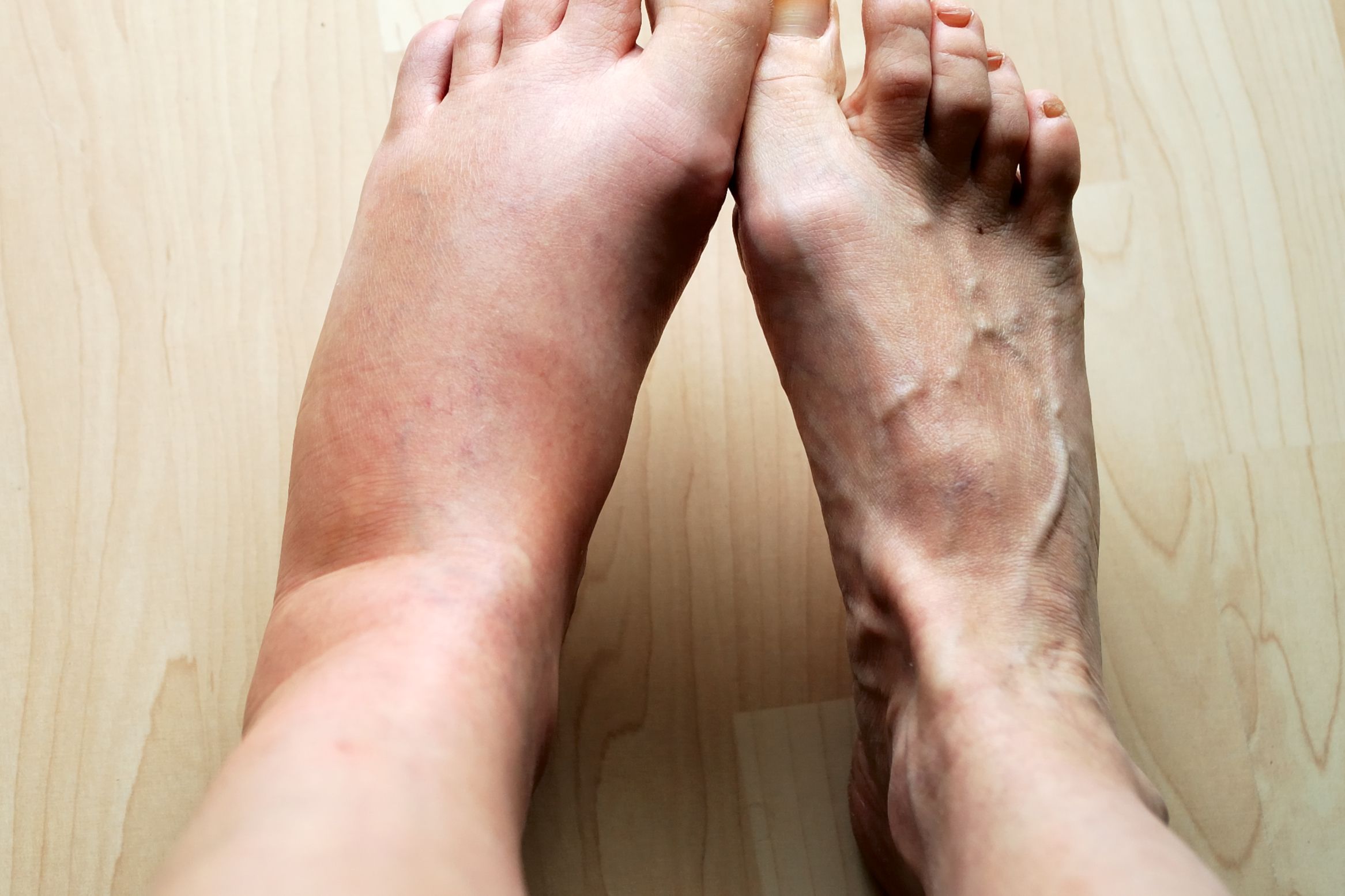
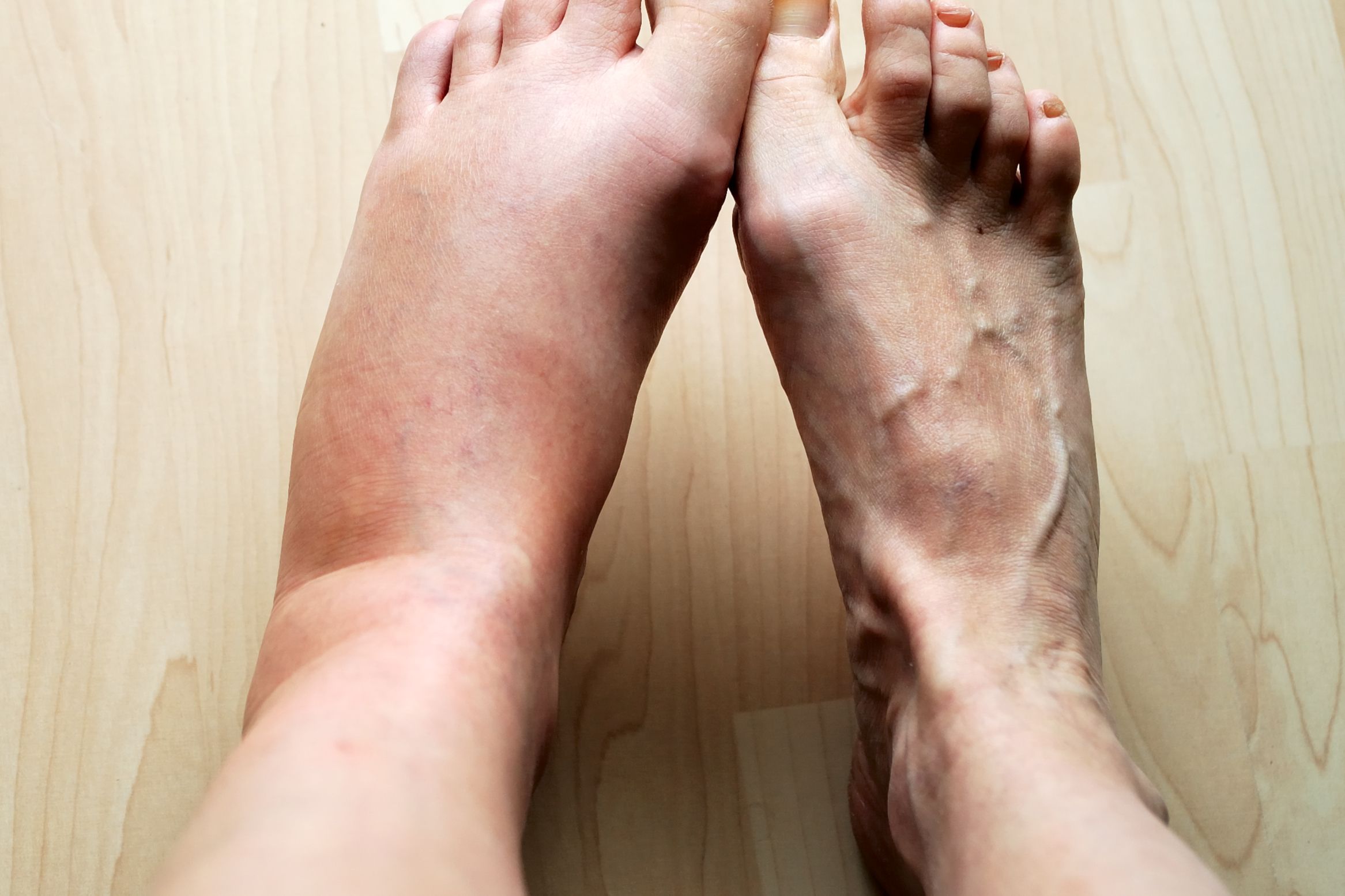
- Swelling that usually affects both legs equally and often involves the feet and ankles
- The skin over the swollen area may be stretched and shiny
- Pressing on the swollen area with a finger will usually leave an indent (pitting)
Inflammation
Causes:
- Injury or Trauma: Sprains, strains, or fractures can lead to localized swelling.
- Infection: An infection in the leg can cause swelling and other symptoms like redness, warmth, and pain.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus can cause inflammation and swelling in the joints or soft tissues of the legs.
- Vein Problems: Varicose veins or thrombophlebitis (a blood clot in a vein) can cause inflammation and swelling.
Symptoms:
- Swelling may be more localized to the affected area
- Often accompanied by other signs of inflammation such as redness, heat, pain, or loss of function
- Swelling from inflammation is usually not symmetrical (unless both legs are equally affected by a condition)
Diagnosis and Treatment
To determine the underlying cause of leg swelling, a medical evaluation is necessary. This might include:
- Physical Examination: Checking for signs of fluid retention or inflammation
- Medical History Review: Discussing any recent injuries, infections, or underlying health conditions
- Tests: Blood tests, urine tests, ultrasound, or other imaging studies to examine the heart, kidneys, and liver function, or to look for blood clots
Treatment will depend on the underlying cause and might include:
- Medications: Diuretics to reduce fluid retention, antibiotics for infections, or anti-inflammatory drugs for pain and swelling
- Lifestyle Changes: Reducing salt intake, elevating the legs when sitting, increasing physical activity, and wearing compression stockings
- Surgical Treatments: In some cases, such as severe varicose veins or blocked veins, surgical interventions may be required
It’s important not to ignore leg swelling. If you notice your legs are swelling regularly, it’s wise to consult with a healthcare provider to get a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.